VPN Tunnel: How Does It Work & Protect Your Privacy etc.
In all probability, the VPN newbies will often see the term “VPN tunnel” but have no idea on what is it, how it works, and what’s the VPN tunneling protocols. That’s where this post comes in to help all make things clear, either before or during the VPN usage.
The necessity to use a Virtual Private Network (aka VPN) is realized by more and more average people because it does help them have some privacy, gain better security and “freedom” on the web, no matter they are working with public Wi-Fi hotspots or other types of limited networks like LAN, WAN, and WLAN. The VPN usage has also surged since the advent of the COVID-19 crisis, the increasing of remote work mode worldwide, and the increasingly severe internet censorship in many countries in recent years.
Why can the VPN service calm people down and increase their peace of mind when browsing online? It should come down to VPN’s unique reliable workflow, which is based on the focus of this post – VPN tunnel.

What Is VPN Tunnel? How Does It Work?
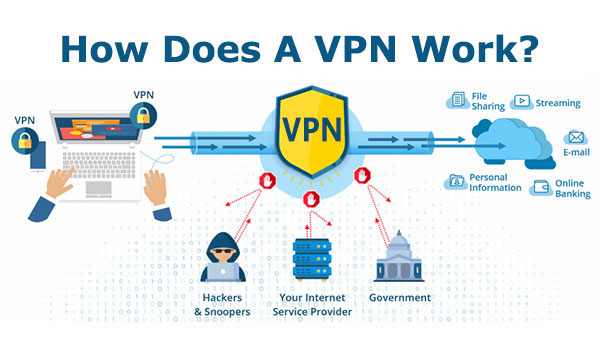
VPN tunnel, simply put, is the encrypted tunnel that connects between the user device and the internet end.
To better understand it, let’s take a look at what is tunneling in computing and VPN separately:
– Tunneling
In computer network, tunneling, commonly known as port forwarding, is a tech method leveraged to connect the same-type networks through another type of network, for example connecting Ethernet 1 to Ethernet 2 via WAN. Tunneling process happens along with the tunneling protocol or say communication protocol, to ensure a successful data travelling by conducting packet encapsulation and wrapping.
Tunneling may rely on layer-2 protocol like PPTP, L2TP and L2F to operate at the data link layer or layer-3 tunneling protocol like IPSec to work at network layer of the OSI model, the former of which is mainly applied for Access VPN/VPDN and the latter of which for In- and Ex-tranet VPN in corporations. There are some other protocol names such as GRE, SSTP, IP in IPv4/IPv6, SIT/IPv6, and OpenVPN.
Generally, the tunneling tech is used to build an accessible or safe path for users to enter into the remote impractical network (e.g. company’s one) or insecure/restricted one. VPN is just a typical service created based on tunneling. Besides, it’s also applied in other places like Linux IP tunneling (Mobile-IP and IP-Multicast) and GPRS Tunnel Protocol/GTP.
– VPN Tunnel
In VPN tech, tunneling refers to the process of data encryption and transport on the public network via VPN tunnel built between two ends, specifically between your device and the network destination. It’s exactly the encryption that makes VPN connections become private, untraceable, and uncrackable. Customer VPN providers may offer varying VPN protocols support, some of which employ known (open source) ones like PPTP, L2TP, IPSec, OpenVPN, and WireGuard while some big brothers simply work out their own unique protocol for claimed better performance. All of them deliver different speed, security, and stability standards. (>> See details on 10 mainstream VPN protocols)
VPNs also use Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) or Transport Layer Security (TLS) that operates at layer 6/7 of the OSI model to establish a secure locked link between the web server and browser, protecting the data on VPN tunnel against third-party’s packet sniffing and man-in-the-middle attack.
Are All VPN Tunnels Private and Secure?
Not exactly.
Whether a VPN’s tunnel or say tunneling process is 100% locked and safe is decided by the VPN protocol plus VPN encryption method the developer adopts and you select to use finally. Only when they two are both strong enough can you enjoy first-class privacy protection. Every VPN protocol has its own pros, cons, and internal encryption. At present, OpenVPN and WiredGuard, plus high-bit encryption like AES and ECC are considered as the most reliable combinations. AES belongs to the symmetric encryption algorithm with truly stronger encryption whereas ECC is asymmetric encryption means with faster speed. If an asymmetric one wants to obtain the same level of cryptographical effect, it would require a longer key length.
Also, end-to-end encryption is essential to keep the communication line totally concealed. Some VPNs only lock the data between the device and VPN server, leaving the left VPN server to website out of VPN tunnel’s protection, that’s so dangerous that data leakage could happen at any time, especially when the site doesn’t use HTTPS yet. Hence take care when selecting a VPN for daily crucial internet activities.
Split Tunneling: A Common VPN Feature to Define What Traffic Goes Through VPN
Split tunneling is basic functionality for a quality VPN program currently. Then what is split tunneling? In short, it’s developed to enable users to customize whether to have all traffic routed via VPN or not. If certain traffic or apps are expected or not expected to use VPN, users just need to enable the split tunneling feature and self-define the details as the VPN requires them to.

What’s the benefit of split tunneling? Once it distinguishes what to use or bypass VPN as you wish, the traffic using VPN will be encrypted and run over VPN tunnel in the private network while not using VPN will still go through the public network as normal, without protection. In this way, you can enjoy both the best local network performance and secured access to the target sensitive, important, geo-blocked websites or content, no need to sacrifice the overall web surfing experience (specifically the connection speed) at all. Yes, to avoid some performance issues and save bandwidth are two main benefits of it.
However, since every coin has two sides, turning on split tunneling may still put you at a security risk. If partial traffic and apps are left to run as usual, the ISPs, hackers, and so forth are still possible to trace your behaviors, snoop your traffic and break into the device locally. That’s why some companies and people with special “really secret” things to do online or are out with public unsafe Wi-Fi tend to disable split tunneling and direct all things through VPN, even they may suffer from the performance hit. That’s because
Not all VPNs generate split tunneling in the same way. Some list all apps directly and have you pick what to be protected by VPN while some provide more ready-made options for one-click confirmation.
FAQs on VPN Tunnel and More
1. Is VPN Tunneling Illegal?
VPN tunneling is just a piece of tech. The legality of this tech should go to that of its further usage like VPN service.
VPN itself is legal in most countries over the world, such as the US, UK, Canada, France, Germany, etc. But if you commit cybercrimes with VPN online, like carrying out ransomware attacks, hacking, phishing, or sharing pirated content, you will still be positioned by the police for further actions. Of course, some heavily-censored countries ban the (usage of) VPN, like South Korea, Turkmenistan, Belarus, Turkey, China, Russia, and the United Arab Emirates, among which a few only permit VPN usage with government approval.
2.What’s the Difference Between VPN and VPN Tunnel?
VPN is a service/tool many individuals and companies leverage for better net privacy, security and freedom. And VPN tunnel means the encryption connection among your machine, VPN server and target network. The process that VPN tunnel works is calling tunneling.
3.Any Recommendation on VPN with Strong Tunneling Ability?
Here PandaVPN is suggested for its simplicity, fast-speed, and stability, even in nations with quite restricted online freedom. Now it has over 3000 accelerated servers in 80 countries and 170+ locations. OpenVPN, Shadowsocks and more strong protocols are embedded for flexible selection. The split tunneling feature is also available to have all or partial data go over VPN tunnel as you like.
Supported platforms: Windows, macOS, Linux, iOS, and Android (TV)
Log policy: 100% no-log policy
Multi-connection simultaneously: Y
Split tunneling: Y
Others: 7-day refund guarantee | 24*7 tech customer support
4.Free vs. Paid VPNs, Do They Share the Same VPN Tunnel?
It depends. Since the free and paid VPNs from a company may have different VPN tunnel configurations, not to mention the ones from hundreds of VPN providers all over the world. The truth is many free VPNs and even a portion of paid VPNs earn profit by compromising users’ privacy, and it’s not wired to see cases on VPN users’ data breach. Therefore, obtaining a quality and reputable VPN with a large user base like PandaVPN is quite necessary.
 Vic Knott
Vic Knott  2022.03.10
2022.03.10 











