What’s Split Tunneling of VPN? When You Need It & Any Security Risk?
Beginners may have no clue on what is Split Tunneling or Split-Tunneling-embedded VPN? This post will explain them in detail and showcase to you some best VPN options that have this functionality.
It’s not a secret that our digital information is the target of many parties, say tech titans, governments, small businesses and hackers. Therefore, it’s not strange still that more customers start to value their online privacy, especially when handling with some sensitive information. Speaking of online privacy protection, the very top choice for most people to leverage is the VPN service, which is able to build up an encrypted VPN tunnel between the device and network so that the all data from the device end can be locked tightly and be untraceable by others.

What’s (VPN) Split Tunneling?
Before we get into the concept of split tunneling, let’s first have a look at what is tunneling in networking.
In the virtual world, tunnels refer to the way to transport data with protocols between different networks. So tunneling is of course the process to move data from one network to another. And as the name implies, the concept “split tunneling” means breaking the tunneling into parts, allowing you to access different types of networks at the same time.
As to what is VPN split tunneling, it simply means the way that some (app/website) traffic is routed via the encrypted VPN connection while the left is not and goes through the local network connection directly.
Different Types of VPN Split Tunneling
Usually, there are two ways to realize split tunneling in VPN service. Below are the paths in detail:
- • App inclusion or exclusion for VPN connection
Basic commercial VPN software will route all traffic via the VPN tunnel. But since VPN will affect the connection speed to some degree and some users don’t want to have VPN connection influence their normal app usage (especially referring to those with no privacy protection or acceleration demand), quality tends to embed split tunneling feature based on application. You can customize which app(s) to use or not use a VPN connection so that you can enjoy a higher level of privacy and Internet speed at the same time. For example, you can just enable VPN for your Email app when sending sensitive data but leave it off other apps and have them access local connection still.
- • Defining URL/Link to enable or disable VPN
Set aside app specifying, routing, or not routing certain URL(s) is also available on browser-based VPN extension or VPN applications that are preloaded with this function. In short, if you only need to use VPN when browsing some special websites, like Netflix web version, torrent sites, adult sites, etc., you can list the link(s) of the target website(s) by following the VPN’s rule and make it effective at any time you want.
Note: Sometimes we can see another term inverse split tunneling, it’s not a new method actually, but refers to the way to define what apps or webpages don’t be routed with VPN. Exactly, the “app exclusion” and “defining URL/link to disable VPN” belong to inverse split tunneling.
How does Split Tunneling Work in VPN?
From the content above, you may have a general understanding of the workflow of VPN split tunneling. Now let’s dive deep into it with an infographic.
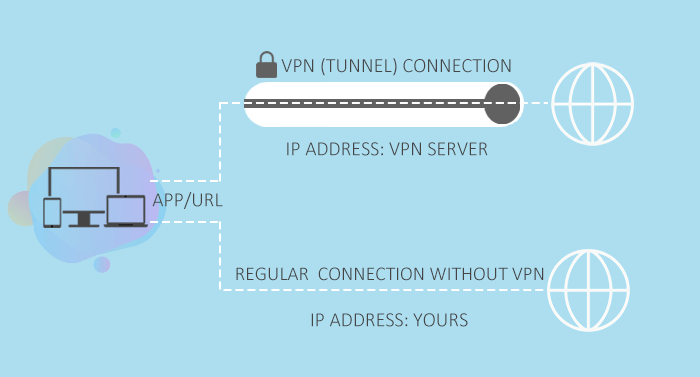
Split-tunneling-enabled VPN works just like the image above shows. You firstly decide traffic from which apps or links should be safeguarded with VPN or should keep using the local internet in the VPN client, then when your device is connected with the VPN server successfully, the VPN will do as you’ve configured before. Surely if you don’t do related settings, the VPN will route all internet traffic through the encrypted tunnel by default, securing your data and identity comprehensively and hiding them from the watchers.
Is Split Tunneling Necessary for VPN? Pros and Cons Shared
In general, split tunneling is a common advanced VPN feature. That said, if the VPN provider is devoted to offering its users high-quality VPN service, Split Tunneling is quite necessary. For common users, “something is better than nothing” since nobody knows when this function is badly needed, such as:
– when you redirect all traffic with VPN, the overall connection speed may be decreased, causing some lag or freezing issue when using some applications, surfing some websites, doing file download, or media streaming).
– when you want to access foreign web content, for instance, the US Netflix and geo-blocked P2P sites, while still keeping the search engine results locally.
…
Therefore, leveraging split tunneling at the right time will offer you pros like:
– adding additional security to selected apps or websites
– enabling you to personalize the VPN connection at will and enjoy both local and the outside network simultaneously, in two IP addresses.
– delivering you a better Internet speed (compared to full tunneling), etc.
But there are still some cons for applying VPN split tunneling, say:
– the apps or URLs out of the VPN tunneling range are not protected at all so that third parties like ISPs, governments, advertising agencies and hackers are able to track you as normal.
– it’s hard for the school, libraries, companies, and so forth with network restrictions to monitor and control the behaviors of connected members.
Best VPN Picks That Support Split Tunneling
Many top-ranked VPNs has split tunneling feature but the supported platforms vary from one to another, just like ExpressVPN has app-based tunnel splitting in Windows, Android, and macOS (11+) systems, NordVPN features it still on Android and Windows devices, and Surfshark VPN names it as “Bypasser” for you to include or exclude traffic on Windows and Android app.
Here we recommend another best pick with the full support of split tunneling in its different version if this is a core feature when you choose a VPN, and its name is PandaVPN.
PandaVPN is now available on Windows, macOS, iOS, Android (TV), and Linux. All PC versions provide you settings on URL-based split tunneling or inverse split tunneling while mobile versions the app-based ones.
How to use VPN split tunneling on Windows, macOS and Linux with PandaVPN
Step 1: Download, install, and launch PandaVPN for your desktop or laptop. Account sign up and login is required to go ahead.
Step 2: Choose a route mode. To obtain the highest level of data encryption, you are suggested to use Global VPN Mode.
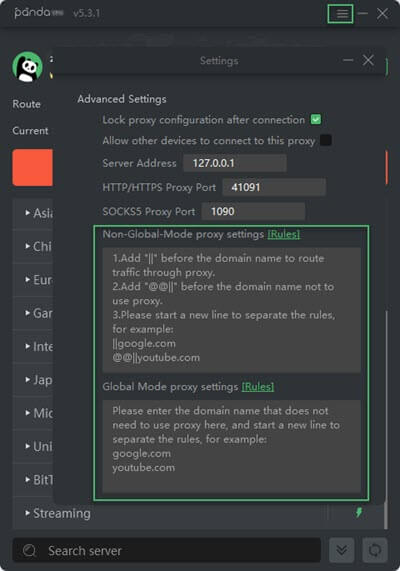
Step 3: Click the three-line icon on the top interface and choose Settings to pup up another Settings window. Then Navigate to the Advanced Settings section, and input the splitting rules by following the guidance at “Non-Global-Mode proxy settings” or “Global-Mode proxy settings” according to your actual situation.
Step 4: Close the Settings panel and choose a server to connect immediately. This way, when you visit the domain names you’ve listed at the settings, the traffic will be routed or not as you wish.
How to use VPN split tunneling on Android and iOS with PandaVPN
Step 1: Have PandaVPN downloaded and installed on your gadget. Create a digital account and log it in.
Step 2: You can pick a route mode at this time or later on. Then click the settings icon on the top corner to expand the menu, where you need to tap the last Settings to enter into a dedicated panel.
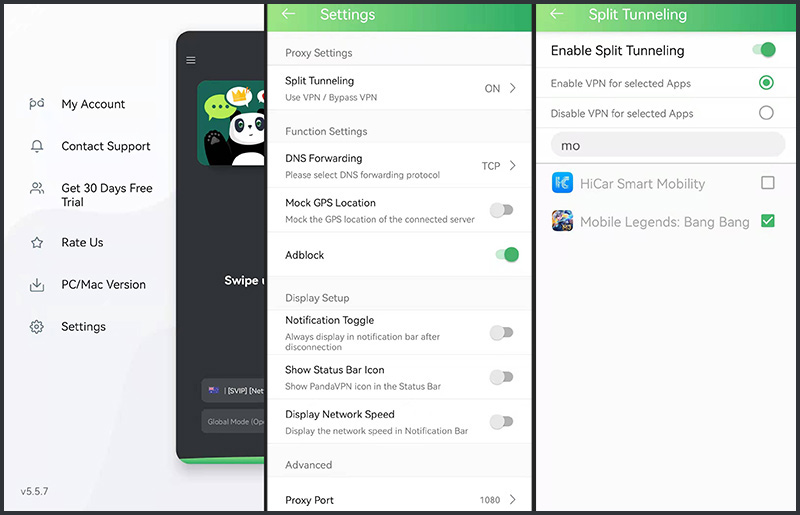
Step 3: Tap Split Tunneling and enable it. After that , “Enable VPN for selected Apps” and “Disable VPN for selected Apps” choices will show up. You just tick the one you’d like to do and then related app name(s) from the app list.
Step 4: Once you’ve done the selection, go back to the main interface and swipe the button up to connect with an expected VPN server. Connection successful, you are free to handle sensitive data with VPN protection and the left out of VPN routing.
 Vic Knott
Vic Knott  2022.01.21
2022.01.21 










